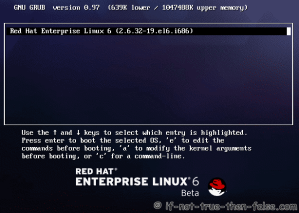
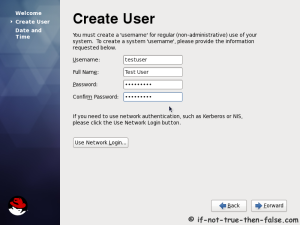
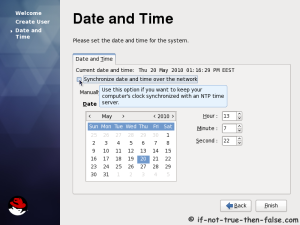
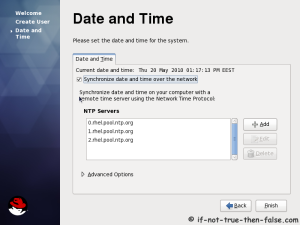
This is Red Hat 6 RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux) installation guide, step-by-step walkthrough with screenshots. Current version of Red Hat 6 is Beta, but also this RHEL 6 Beta version looks very stable and good OS, so that’s why I decided to write this RHEL 6 Installation guide.
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Beta is available on the following architectures:
- i386
- AMD64/Intel64
- System z
- IBM Power (64-bit)
Download Red Hat 6 Beta DVD images here.
- i386
- AMD64/Intel64
- System z
- IBM Power (64-bit)
Download Red Hat 6 Beta DVD images here.
Some of the many improvements and new features that are included in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
- Power management – tickless kernel and improvements through the application stack to reduce wakeups, power consumption measurement by Powertop, Power Management (ASPM, ALPM), and adaptive system tuning by Tuned, all enhance more efficient system power usage.
- Next generation networking – comprehensive IPv6 support (NFS 4, CIFS, mobile support [RFC 3775], ISATAP support), FCoE, iSCSI, and a new and improved mac 802.11 wireless stack.
- Scalable filesystems – ext4 file system provides support for larger file sizes and significantly reduces repair times over ext3. XFS® is a high-performance file system that supports extremely large files and is optimized for large data transfers.
- Virtualization – KVM includes performance improvements and new features, sVirt protects the guest and host from unauthorized access, SR-IOV and NPIV deliver high-performance virtual use of physical devices, and libvirt leverages kernel resource management functionality.
- Enterprise security enhancement – SELinux includes improved ease of use, application sandboxing, and significantly increased coverage of system services, while SSSD provides unified access to identity and authentication services as well as caching for off-line use.
- Development and runtime support – SystemTap improvements, ABRT is a new framework for simple collection and reporting of bug information, and improvements are made to GCC (version 4.4.3), glibc (version 2.11.1), and GDB (version 7.0.1).
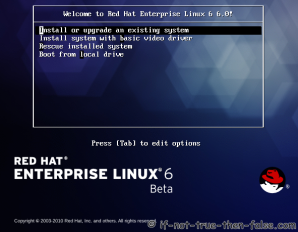
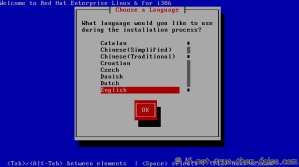
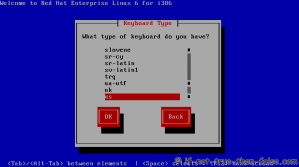
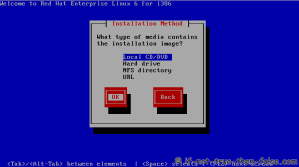
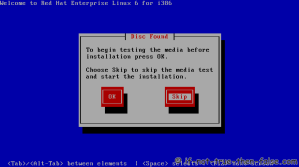
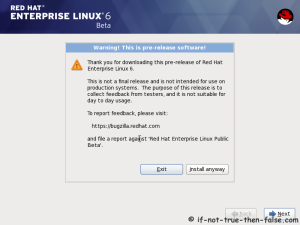
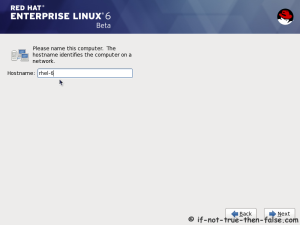
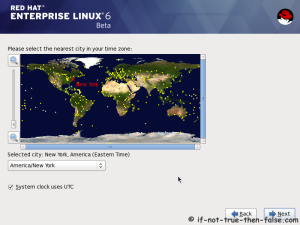
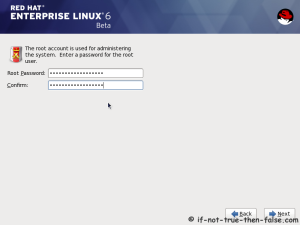
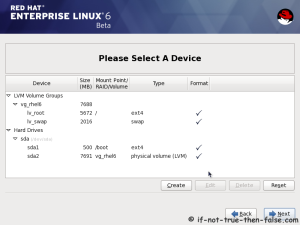
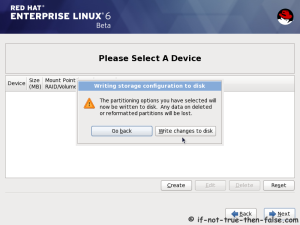
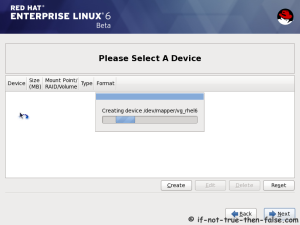
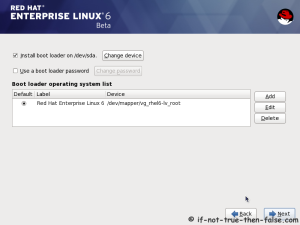
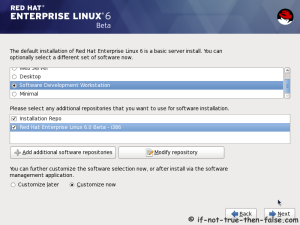
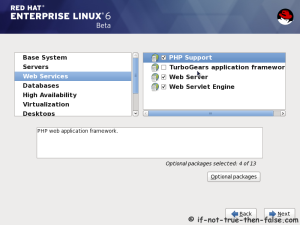
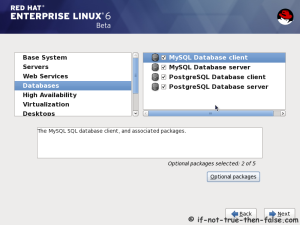
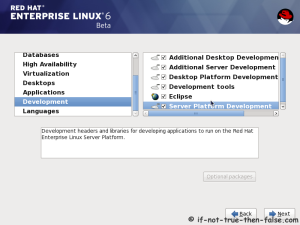
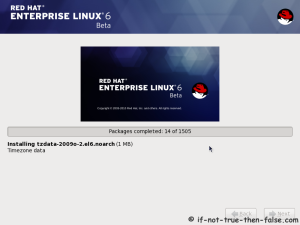
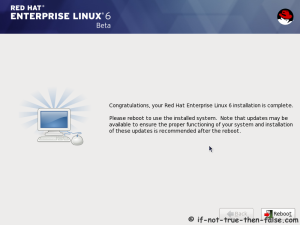
On this guide I use Graphical Installer. There is also Kickstart automated installation method and Text-based Installer available. And I install this machine for Software Development Workstation and testing environment. So package selection is following: Desktop, Web server, Databases, Compiling tools, Java. Same method works also for servers, normal desktops and other setups, but of course different software selection. So let’s begin installation…
- Power management – tickless kernel and improvements through the application stack to reduce wakeups, power consumption measurement by Powertop, Power Management (ASPM, ALPM), and adaptive system tuning by Tuned, all enhance more efficient system power usage.
- Next generation networking – comprehensive IPv6 support (NFS 4, CIFS, mobile support [RFC 3775], ISATAP support), FCoE, iSCSI, and a new and improved mac 802.11 wireless stack.
- Scalable filesystems – ext4 file system provides support for larger file sizes and significantly reduces repair times over ext3. XFS® is a high-performance file system that supports extremely large files and is optimized for large data transfers.
- Virtualization – KVM includes performance improvements and new features, sVirt protects the guest and host from unauthorized access, SR-IOV and NPIV deliver high-performance virtual use of physical devices, and libvirt leverages kernel resource management functionality.
- Enterprise security enhancement – SELinux includes improved ease of use, application sandboxing, and significantly increased coverage of system services, while SSSD provides unified access to identity and authentication services as well as caching for off-line use.
- Development and runtime support – SystemTap improvements, ABRT is a new framework for simple collection and reporting of bug information, and improvements are made to GCC (version 4.4.3), glibc (version 2.11.1), and GDB (version 7.0.1).